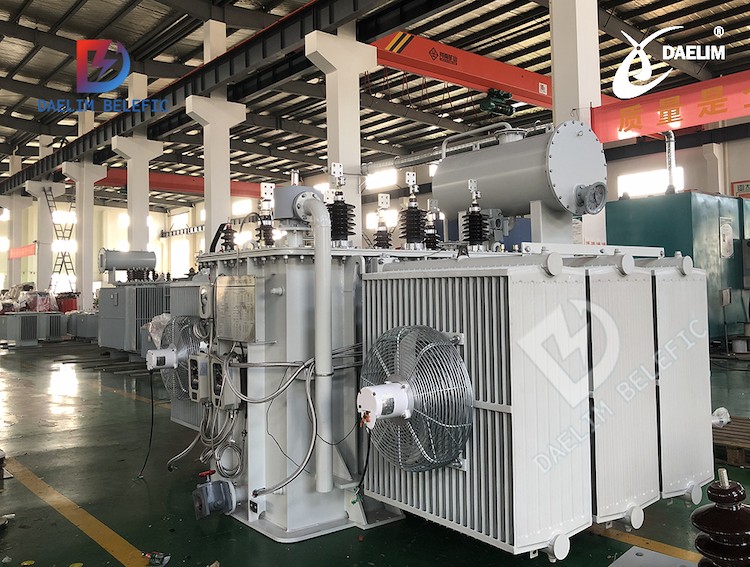
The Ultimate Guide to Electric Transformer
 There are various types of transformers used for different purposes, including electric transformers, test transformers, instrument transformers, and special-purpose transformers. In this article, we will focus on electric transformers, which are essential for transmitting and distributing electrical power to homes and businesses.
There are various types of transformers used for different purposes, including electric transformers, test transformers, instrument transformers, and special-purpose transformers. In this article, we will focus on electric transformers, which are essential for transmitting and distributing electrical power to homes and businesses.
Daelim Transformer is a professional manufacturer of electric transformers. They are proficient in various international standard technologies, such as ANSI, IEEE, CSA, IEC 60076, AS, GOST, and EN 60076. Daelim Transformer has obtained certificates including UL/cUL, CSA, CESI, and others.

High voltage up to 345kV and power rating up to 500MVA;
According to ANSI/EEE, IEC, CSA, and AS as well as NEMA standards

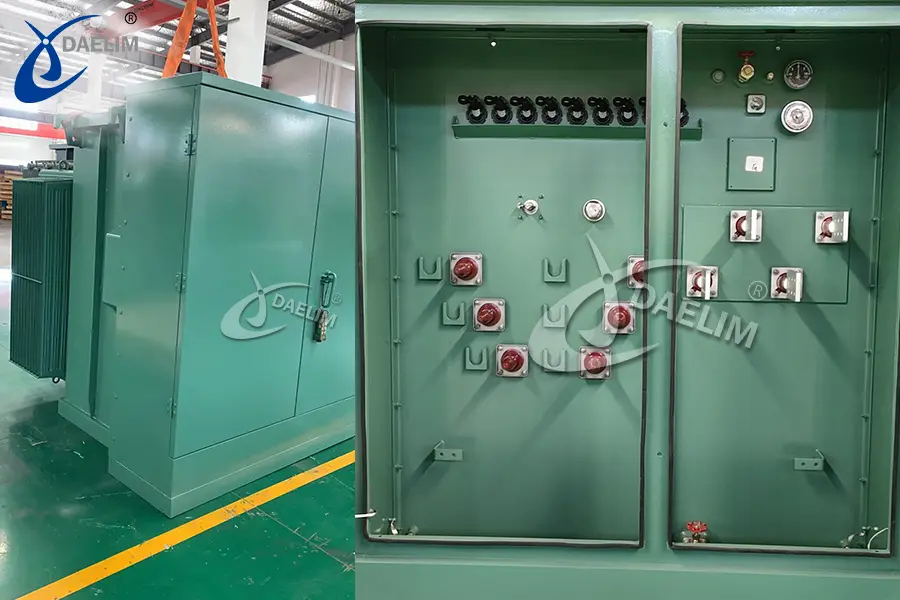
Single Phase: High voltage up to 34.5kV and power ranting up to 250 kVA
3 Phase: High voltage up to 44kV and power ranting up to 10000 kVA with UL listed

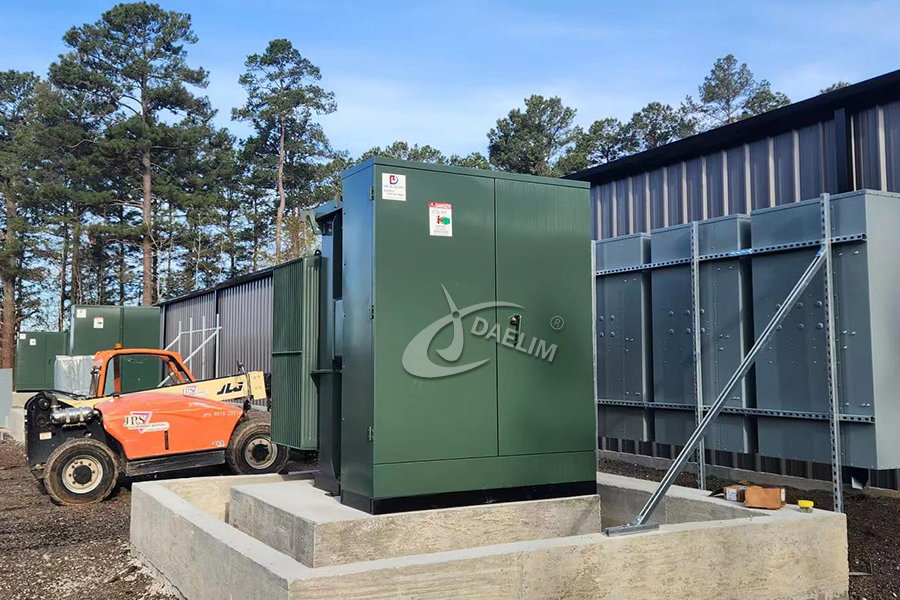
High voltage up to 46kV and power rating up to 20MVA with UL listed
Standards: ANSI, IEEE, CSA, AS, NZS, IEC
What is an electric transformer?
An electric transformer is a device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to change the AC voltage and distribute or transmit electrical energy without changing the frequency. It transfers electric energy between systems with multiple windings.
Learn more: Basic Guide Of Electrical Transformer
What does an electric transformer do?
Electric transformers have a wide range of applications. They are utilized in data centers, renewable energy systems, battery energy storage systems (BESS), oil and gas exploration, as well as commercial and residential areas.
In power systems, the transmission of electric energy incurs voltage and power losses. When installing transformers, it is essential to choose a suitable location that allows for convenient operation, maintenance, and transportation while prioritizing safety and reliability.
Read more: Electric Power Substation Transformers
Where is the electric transformer located?
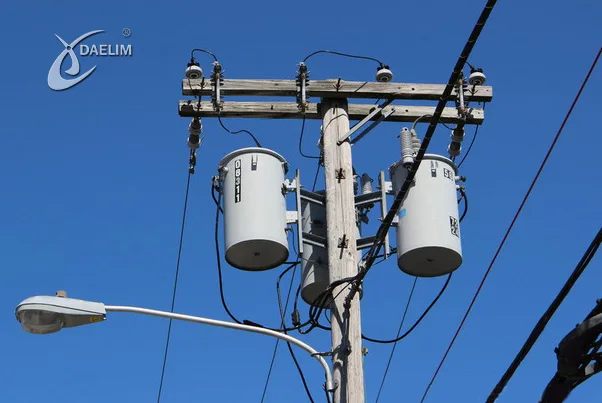 Electric transformers are crucial components of power distribution infrastructure, found in various locations such as substations, power plants, industrial sites, utility poles, and urban areas. They play a vital role in stepping up or stepping down voltage levels to ensure safe and reliable electricity supply to residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
Electric transformers are crucial components of power distribution infrastructure, found in various locations such as substations, power plants, industrial sites, utility poles, and urban areas. They play a vital role in stepping up or stepping down voltage levels to ensure safe and reliable electricity supply to residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
In urban settings, electric transformers are commonly seen in residential areas, parks, and near establishments like hotels. These transformers support localized power distribution by regulating voltage and ensuring a consistent electricity supply for lighting, amenities, and other needs.
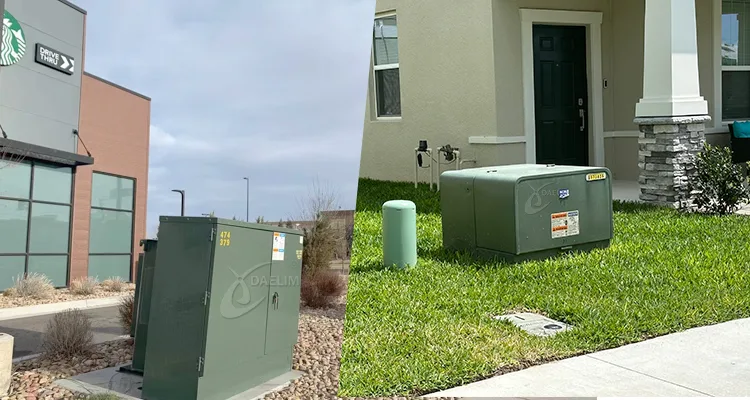

For instance, in parks, transformers enable efficient distribution of electricity for lighting and recreational facilities, enhancing visitor experience. Transformers manage voltage levels near hotel entrances to maintain uninterrupted power supply throughout the premises.
Electric transformers near charging stations for electric vehicles (EVs) are also instrumental in converting grid electricity to suitable levels for EV charging. They contribute to the safety and efficiency of charging operations, facilitating convenient access to electric vehicle charging facilities.
5000kVA 12kV Pad Mounted Transformer For EV Charging Station

How does an electric transformer work?
All electric transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The voltage is increased or decreased by the ratio of the coil turns of the primary and secondary windings.
Try for free: How To Choose The Suitable 110KV Power Transformer?
How many types of electric transformers are there?
Classification according to installation methods
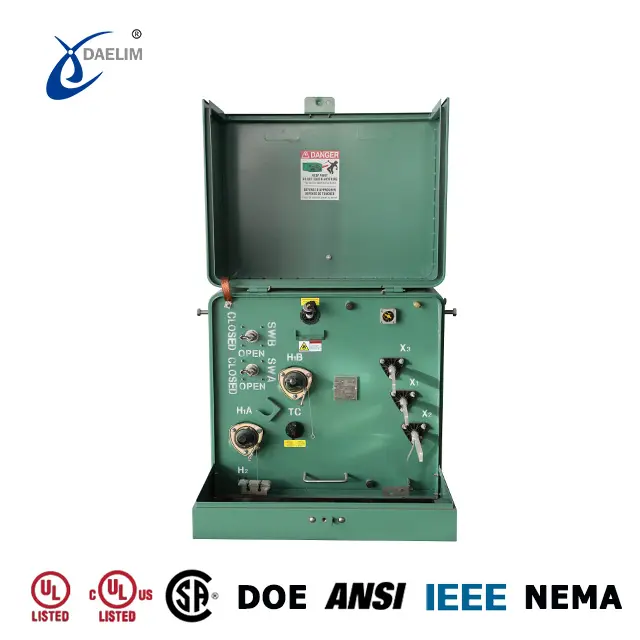
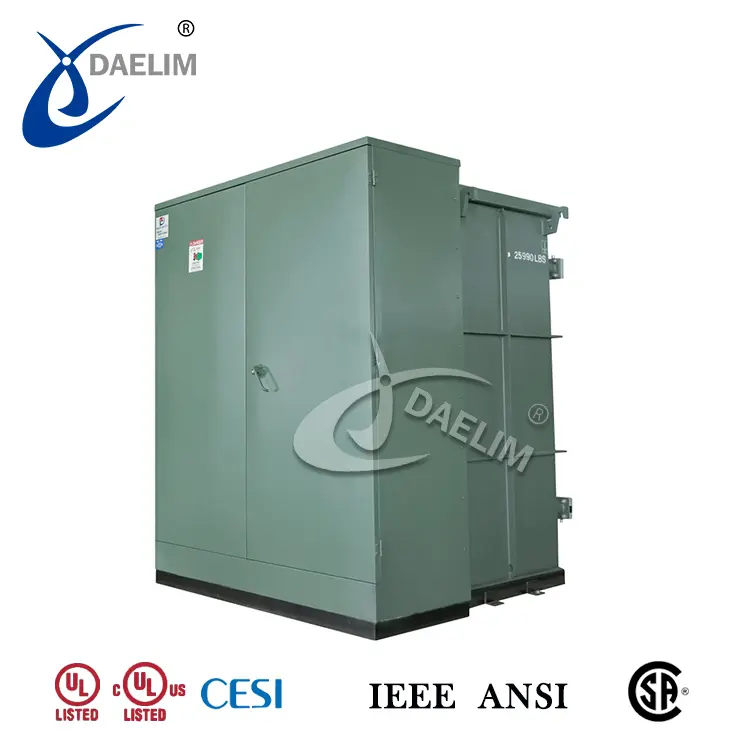
Electric transformers can be categorized as pole-mounted transformers and pad-mounted transformers.
Pole-mounted transformers are affixed to utility poles, providing a compact and elevated solution for power distribution. These transformers are commonly seen along utility lines and are often used in areas where space is limited or underground installation is not feasible.
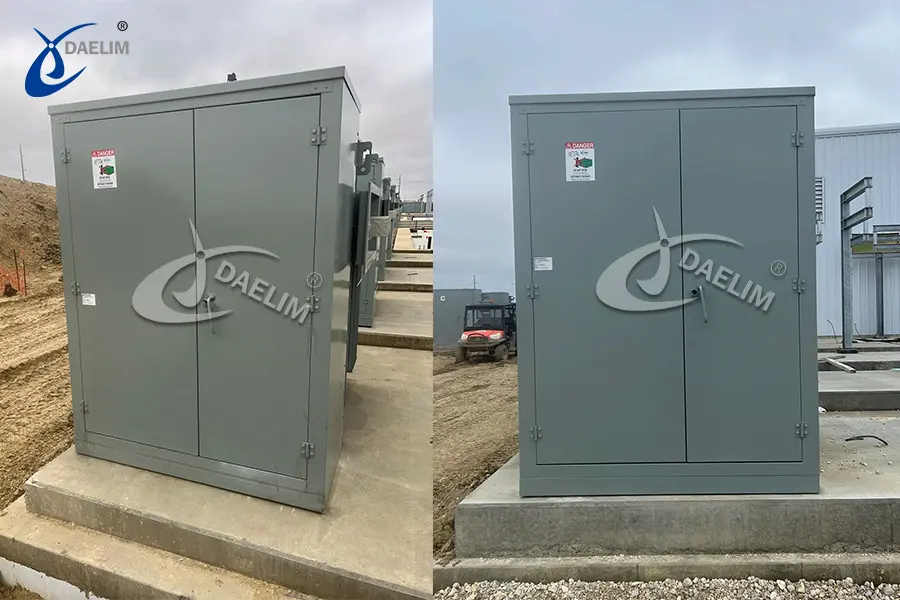
On the other hand, pad-mounted transformers are installed at ground level on concrete pads or enclosures. This type of transformer offers a more secure and visually discreet option. They are typically employed in urban areas, residential neighborhoods, and commercial settings where aesthetics and safety considerations are important.
Both pole-mounted and pad-mounted transformers play integral roles in ensuring efficient power distribution and meeting the diverse needs of electrical systems in various locations.
You may enjoy: Single Phase Pad Mounted Transformer
What is the construction of an electric transformer?
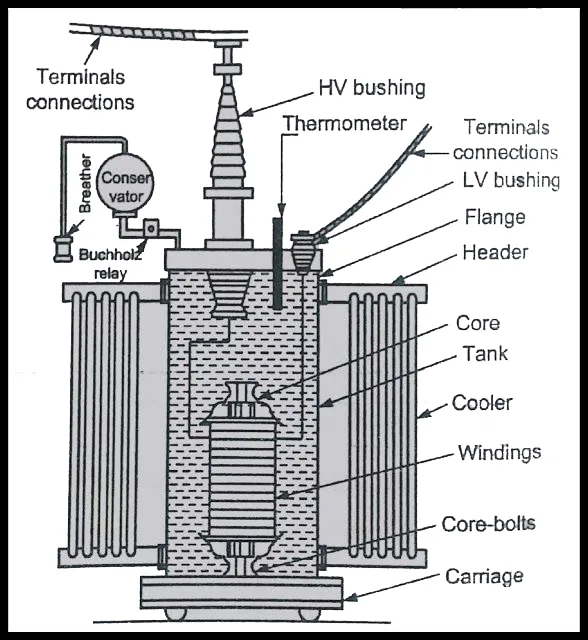 An electric transformer comprises various essential components that work together to enable its operation:
An electric transformer comprises various essential components that work together to enable its operation:
Coil: The coil forms the magnetic circuit of the transformer and consists of insulated copper or aluminum wire. It plays a critical role in creating the electromagnetic field necessary for the transformation of electrical energy.
Winding: The winding is the circuit component of the transformer, connected to the coil. It allows for the flow of electrical current and facilitates the transfer of energy between the primary and secondary coils.
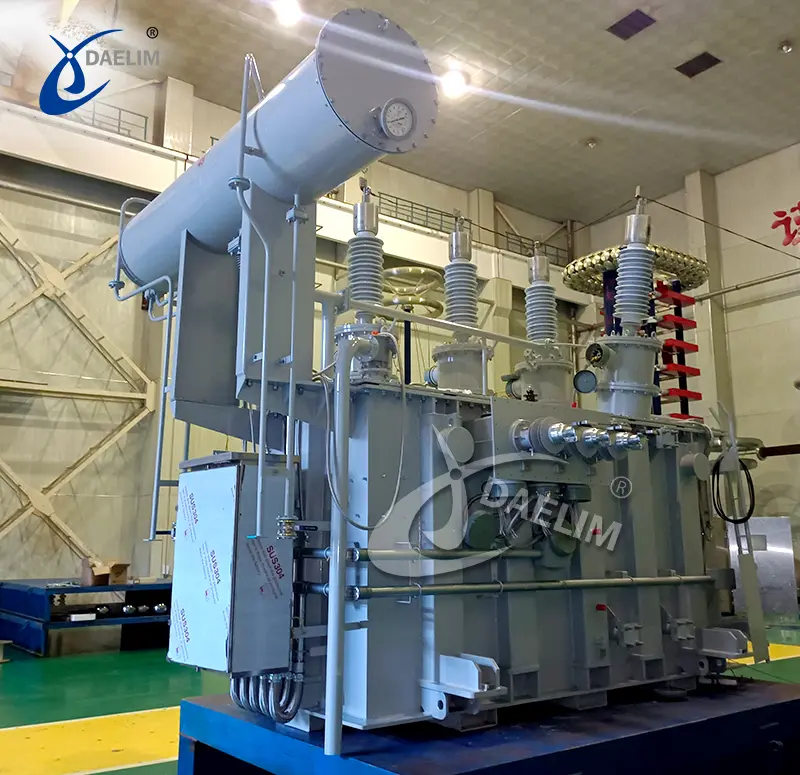
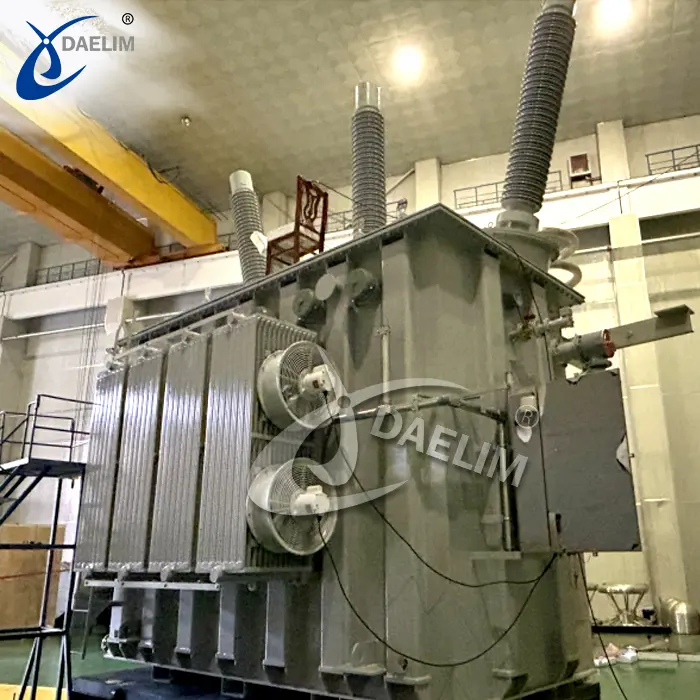
Iron core: The iron core is an integral part of the transformer, working in conjunction with the coil and winding. It forms the electromagnetic field and assists in the efficient conversion of energy from one voltage level to another.
Transformer oil tank: The transformer oil tank houses the transformer body and insulating oil. The shape and structure of the oil tank vary depending on the specific type of transformer. For instance, a single-phase pad-mounted transformer typically has a cube-shaped box with a flip cover, while a three-phase pad-mounted transformer has a standing cuboid shape.
Voltage regulating device: Transformers may include non-excitation voltage-regulating switching devices or on-load voltage-regulating switching devices. These devices help control and adjust the output voltage as required.
Cooling devices: Cooling devices, such as radiators and coolers, are employed to maintain optimal operating temperatures within the transformer, ensuring efficient performance and preventing overheating.
Protection devices: Various protection devices are incorporated to safeguard the transformer and ensure its reliable operation. These include an oil conservator, fuse, oil level gauge, safety airway, gas relay, pressure release device, moisture absorber, and oil purifier.
Outlet device: High and low-voltage terminals, as well as cable inlets and outlets, are present to facilitate the connection of the transformer to the power grid and other electrical systems.
Accessories: Different types of transformers may require specific accessories. Examples include high and low-voltage terminals, fuses, and other components specific to pad-mounted transformers.
By incorporating these components and accessories, electric transformers are able to efficiently transform electrical energy, ensuring reliable power distribution in various applications.
Try for free: How Much Do You Know For The Different Types Of Transformers?
How long does it take to replace an electric transformer?
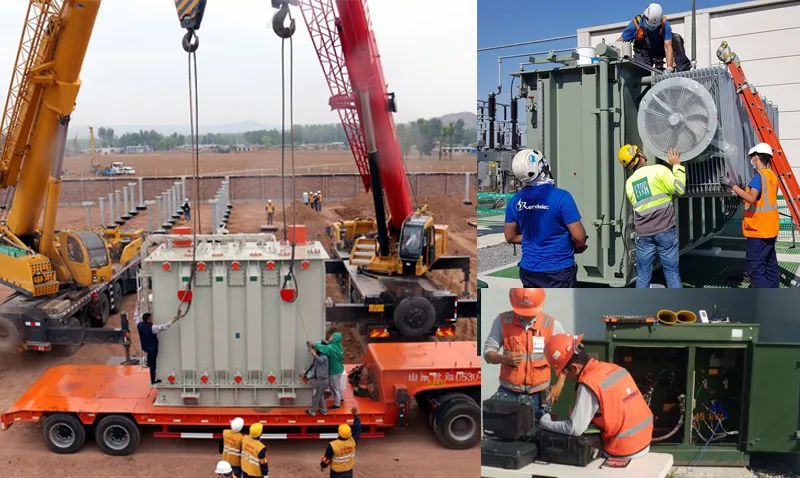

The replacement time for transformers varies significantly based on their types, power ratings, and voltages. For instance, residential transformers can be replaced relatively quickly, often within a few hours, as they are smaller and easier to install and remove.
In contrast, larger high-voltage transformers require a longer replacement time, typically ranging from a few days to several weeks. The complexity of dismantling and installing these transformers necessitates extensive preparation work, including the mobilization of mechanical equipment and manpower. This meticulous approach ensures a smooth and safe replacement process for these critical components of the power system.
Read more: Substation Transformer
Why an electric transformer explosion?
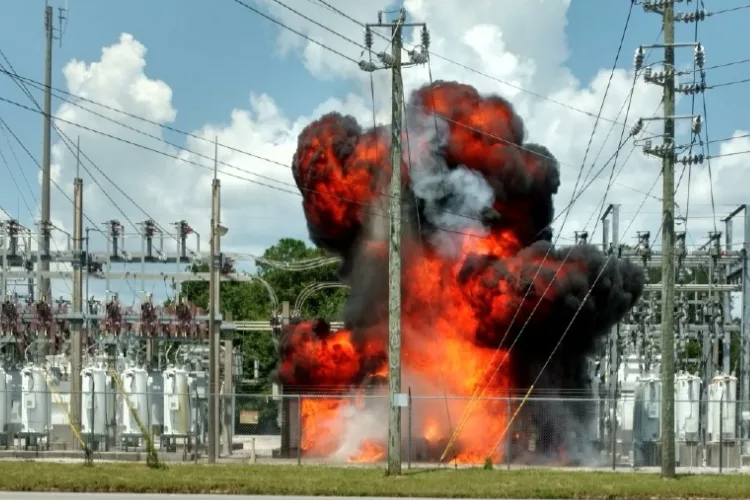

Electric transformer explosion can result from both internal and external causes. Internal factors include insulation damage, aging coil insulation, poor contact, and load short circuit overheating. External factors involve lightning overvoltage and external fires.
Insulation damage: This occurs due to aging coil insulation, inadequate oil levels, poor soil quality, core insulation aging, insufficient maintenance, or physical damage to insulation.
Poor contact: Loose bolts, unstable welding, or contact damage to the tap switch can lead to local overheating, insulation damage, short circuits, and the rapid decomposition of insulation oil, generating gas and pressure surges.
Lightning overvoltage: High-voltage surges caused by lightning strikes can break down transformer insulation, resulting in burnout or fire.
Load short circuit: If a transformer experiences a significant short-circuit current due to a load short circuit, it may be damaged or burned if the protection system fails or the settings are incorrect. Installing a short-circuit protection device and using appropriate fuses can mitigate such risks.
Transformer overheating: Overheating can affect the transformer's lifespan and, in severe cases, lead to fuel injection, combustion, or explosion. Causes of overheating include high contact resistance, excessive operational load, increased iron loss due to high voltage, high ambient temperature, and poor ventilation.
External fire ignition: Transformers can catch fire when nearby combustible materials ignite and spread to the transformer or its chamber.
It is important to note that inadequate contact and short-circuit overheating are common causes of transformer explosions. Undersized transformers or heavy loads can increase the risk of such incidents. Therefore, transformer selection should carefully consider capacity requirements.
By understanding these causes of transformer damage, appropriate measures can be taken to prevent or mitigate the risks, ensuring the safe and reliable operation of transformers within electrical systems.
Keep reading: Analysis of electric transformer noise problem
How to prevent electric transformer explosion?
To minimize the risk of electric transformer explosion, implementing preventive measures is crucial. Consider the following:
Transformer oil selection: Choose electric transformer oil specifically designed for enhanced safety, with a low ignition point to reduce fire hazards.
Regular inspections: Conduct periodic assessments to identify any signs of damage or deterioration, including insulation condition, loose connections, abnormal heating, and oil levels.
Maintenance practices: Implement a comprehensive maintenance program that includes cleaning, testing, tightening connections, and replacing worn-out components to prevent failures.
Temperature monitoring: Install temperature monitoring systems to detect abnormal temperature rises, indicating potential issues or overheating.
Protection systems: Ensure the transformer has reliable overcurrent and short-circuit protection devices. Regularly test and calibrate these systems to ensure their effectiveness.
Fire prevention measures: Implement measures to prevent fires, such as maintaining adequate clearance from combustible materials, installing fire-resistant barriers, and ensuring proper ventilation for heat dissipation.
By employing these strategies, including selecting appropriate electric transformer oil, conducting regular inspections and maintenance, monitoring temperatures, implementing effective protection systems, and adopting fire prevention measures, the risk of transformer damage can be significantly reduced. These measures contribute to the safe and reliable operation of electric transformers in electrical systems.
Try for free: Comprehensive Guide to 1000kVA Transformers
What price of an electric transformer?

The price of electric transformers can vary significantly due to several factors, including capacity, voltage, frequency, connection type, cooling method, impedance, no-load loss, full load loss, presence of NLTC or OLTC, standards compliance, work frequency withstand voltage, and lightning impulse withstand voltage.
If you have specific requirements for electric transformers, you can contact Daelim Transformer. Their experienced team will promptly provide you with an accurate price quote tailored to your needs. Daelim Transformer specializes in delivering customized transformer solutions and ensures quick response times. By reaching out to Daelim, you can expect efficient and reliable service, enabling you to obtain precise pricing information.
Related Products
Related Article
13.8 kV 10.5 MVA Substation Transformer for Ecuador
A customer from Ecuador contacted Daelim Transformer for a 10.5MVA substation transformer (13.8kV high voltage, 2.4kV low voltage). Daelim Transformer provided a customized solution, conducted virtual factory tours, ensured rigorous quality control via video inspections, and offered post-delivery online training and ongoing support, fostering a successful partnership.
2600 kVA Pad Mounted Transformer for Blcokchain
Daelim Transformer successfully provided three customized 2600 kVA pad mounted transformers to power a state-of-the-art blockchain facility in Texas, USA. Our transformers were meticulously designed to meet the unique demands of the mining operation, ensuring seamless power distribution with unwavering reliability and efficiency.
20MVA Power Transformer for the United States
This project involves the development of a 20 MVA three-phase power transformer tailored for the United States market. The primary voltage is 24.94kV, and the secondary voltage is 4.16kV, indicating it functions as a step-down transformer. The design and production fully comply with IEEE C57.12.00 standards and have passed third-party UL team testing. All accessories also adhere to IEEE standards. FR3 vegetable oil serves as the insulating liquid for the transformers.
1500 kVA Transformer for Australian Mining Project
Introduce the 1500 kVA transformer tailored for Australian mining projects. The transformer operates in a three-phase configuration, with a total of four units deployed. Notably, its primary voltage stands at 11kV, while the secondary voltage is 1kV. Characterized by its compact size, emphasis on safety, and unwavering reliability, this transformer is meticulously designed and manufactured to meet the stringent requirements outlined in AS 60076 and AS efficiency value standards.Let's delve into the key features and specifications of this essential solution.
2 MVA Pad Mounted Transformer for Utility
Behold the backbone of Canada's utility infrastructure—the 2MVA pad mounted transformer. With a primary voltage of 4160Grdy/2400V and a secondary voltage of 800GrdY/461V, this transformer stands as a testament to efficiency and reliability in power distribution. Crafted in strict accordance with CSA standards and CAN/CSA802.1 energy efficiency guidelines, it embodies the pinnacle of engineering excellence.
2600 kVA Pad Mounted Transformer For Blockchain In Kansas
This morning, I received the on-site photos of the pad-mounted transformers from the customer, and I was overwhelmed with excitement and joy. These pad-mounted transformers are installed at a 20MW blockchain site in Kansas, USA. A total of 5 sets of 2600 kVA pad-mounted transformers, all UL-listed, are being deployed at this site. Currently, 3 sets have already been installed onsite and are scheduled to be powered on imminently.















