A Guide to Radial Feed and Loop Feed Transformers
 Radial feed and loop feed transformers are two types of transformers commonly used in electrical distribution systems. At Daelim Transformers, the main product is 3 phase pad mounted transformers, which are specifically designed to meet the demands of these systems.
Radial feed and loop feed transformers are two types of transformers commonly used in electrical distribution systems. At Daelim Transformers, the main product is 3 phase pad mounted transformers, which are specifically designed to meet the demands of these systems.
The radial feed and loop feed transformers are sealed within an enclosure that features two hinged doors, ensuring that they are safe, tidy, and aesthetically pleasing. As a result, they are often chosen for an installation in urban areas, parks, gardens, and other public spaces.
At Daelim Transformers, we are committed to providing high-quality transformers that not only meet the needs of our customers, but also enhance the visual appeal of the spaces in which they are installed.
What are Radial Feed and Loop Feed?

Radial feed and loop feed are two types of electrical power distribution systems commonly used in transformers. In a radial feed system, power flows from a single source or substation to the loads through a single line or feeder. This means that if there is a fault in the line, the entire system may be affected. In contrast, a loop feed system has multiple sources or substations that are interconnected through multiple lines or feeders, creating a redundant system that allows power to be rerouted in the event of a fault.
In terms of transformers, radial feed transformers are designed to receive power from a single source and distribute it to multiple loads, while loop feed transformers are designed to receive power from multiple sources and distribute it to multiple loads. The choice between radial feed and loop feed transformers depends on the specific requirements of the electrical distribution system and the load being served.
Daelim Transformers offers two types of selections for three phase pad mounted transformers: radial feed and loop feed, which are tailored to meet specific circuit needs. Our transformers are equipped with either aluminum winding or copper winding materials to maximize their efficiency.
Our products comply with the latest industry standards, such as ANSI C57, DOE, CSA C227.4, IEEE C57 and IEC, ensuring that they are safe and reliable for use in a wide range of applications. At Daelim, we prioritize our customers' needs, designing and producing transformers that meet their exact specifications.
We take pride in providing high-quality transformers that feature superior performance characteristics, including high voltage, stable neutral points, low loss, small volume, and cost-effectiveness. Our transformers are also designed with safety and environmental friendliness in mind. Trust us to deliver the best solutions for your electrical distribution system needs.
You may enjoy: Pad Mounted Transformer
What are the differences between radial and loop systems?
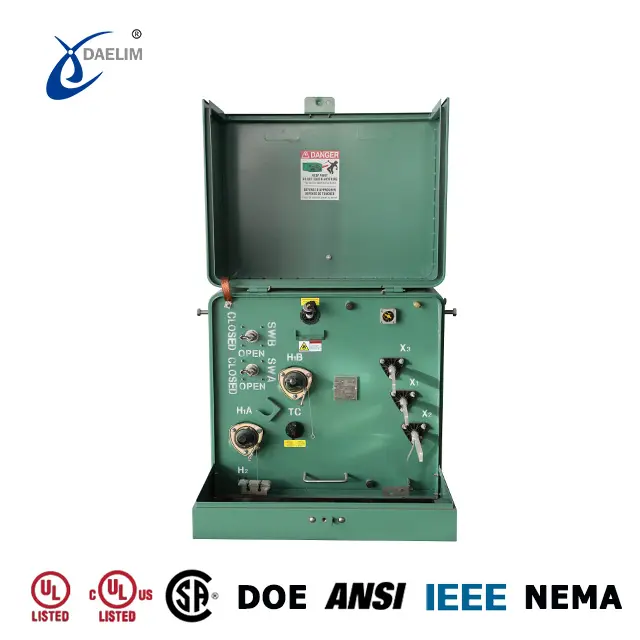
Radial feed and loop feed systems serve the purpose of distributing higher voltage to lower voltage or vice versa. Radial feed transformers typically have three high voltage bushings (H1, H2, H3), while loop feed transformers have six high voltage bushings (H1A, H2A, H3A, H1B, H2B, H3B). Consequently, radial feed transformers have a simpler construction compared to loop feed transformers based on their appearance.
What is a loop feed transformer?
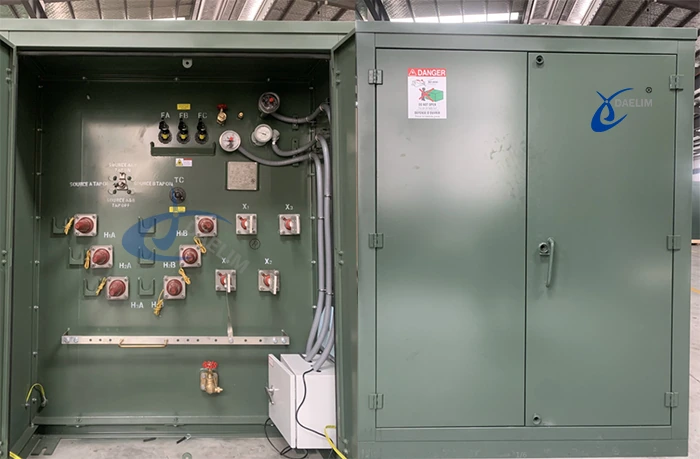
Let's take a closer look at loop feed transformers. Due to their long-term and continuous operation, it is important to minimize the no-load loss and on-load loss of transformers for greater energy efficiency. To ensure safe and cost-effective operation and enhance power supply reliability and flexibility, loop feed pad-mounted transformers are designed.
During low-load seasons, part of the transformer can be stopped, reducing no-load losses and improving efficiency while also lowering reactive excitation current and improving the power factor of the power grid. This leads to improved system economics. If one transformer stops working, the other transformers in the paralleled system continue to operate to ensure uninterrupted power supply. When a transformer needs maintenance or repair, it can be replaced within the parallel system, allowing the transformer to be repaired or taken offline for maintenance without interrupting the main power supply. This approach not only makes transformer repair more convenient but also enhances power supply reliability.
Reading more: Knowing More about A Pad Transformer
How does a loop feed transformer work?
 A loop feed transformer is a type of transformer that is designed to receive power from multiple circuit points, allowing for flexibility in power distribution. Here is a general overview of how a loop feed transformer works:
A loop feed transformer is a type of transformer that is designed to receive power from multiple circuit points, allowing for flexibility in power distribution. Here is a general overview of how a loop feed transformer works:
Wiring Groups: The loop feed transformer typically has multiple wiring groups, which are separate winding sets within the transformer. These wiring groups are connected in parallel, allowing for power to be received from different circuit points.
Transformation Ratio: The loop feed transformer has the same transformation ratio for each wiring group, which means that the rated voltages of the transformer are equal. This ensures that the load is distributed evenly across the different wiring groups when the transformer is loaded.
Load Distribution: When the transformer is loaded, the load is distributed across the different wiring groups in proportion to their rated capacity. This allows for efficient utilization of the transformer's capacity and prevents overloading of any single wiring group.
Circulating Current: When the transformer is not loaded, there should be no circulating current in the winding of the transformer. This is achieved by ensuring that the wiring groups have the same characteristics, such as the same transformation ratio and short-circuit voltage, to prevent circulating currents from being generated.
Redundancy: One of the advantages of a loop feed transformer is that it allows for redundancy. If one wiring group or circuit point fails, the other wiring groups can continue to supply power without interruption, improving the reliability of the power supply system.
Overall, a loop feed transformer provides flexibility in power distribution, load distribution, and redundancy, making it suitable for applications where power needs to be received from multiple circuit points and where reliability and efficiency are important factors.
Loop feed transformers are designed to distribute power to multiple circuits and are typically used in medium-voltage power distribution systems. To ensure that loop feed transformers operate safely and efficiently, it is essential to satisfy certain conditions.
Firstly, the wiring groups of the transformer must be the same to avoid circulating current in the winding when the transformer is unloaded. Secondly, the transformer must have the same transformation ratio, which means that the rated voltages of the transformer should be equal. A difference of ±0.5% is allowed to accommodate manufacturing tolerances.
Thirdly, the short-circuit voltage of the transformer must be equal, with a difference of ±10% allowed. This ensures that the load distribution is proportional to the capacity, and there are no imbalances in the system.
Finally, the capacity ratio of parallel transformers should not exceed 3:1 to limit the short-circuit voltage value of the transformer from being too different from each other. By satisfying these conditions, loop feed transformers can operate safely, efficiently, and reliably, meeting the needs of continuous long-term operation.
You may enjoy: Single Phase Pad Mounted Transformer
What is a radial feed transformer?

A radial feed transformer is a type of transformer used for power distribution that has a simple design with three high voltage bushings (H1, H2, H3). It is used to transfer higher voltage to lower voltage or lower voltage to higher voltage. Unlike loop feed transformers, it does not have multiple sets of high voltage bushings and is not designed for parallel operation. It is commonly used in small to medium-sized power distribution systems, such as in residential or commercial areas.
Radial feed transformers are relatively simpler compared to loop feed transformers, and their design is ideal for a single-point power supply. These transformers have three parallel high voltage bushings, which are typically installed on the left side of the cabinet. However, their simplicity comes at the cost of reduced flexibility, as they can only receive power from one circuit point. Therefore, if there is a need for continuous power distribution from multiple circuit points, a radial feed transformer may not be the best option.
Try for free: How to choose pad-mounted transformer for your project?
How to choose a loop feed or radial feed transformer?

The choice between a loop feed and radial feed transformer depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the power distribution system. Here are some factors to consider:
Load characteristics: If the power demand is relatively constant and can be served by a single circuit point, a radial feed transformer may be more suitable. However, if the load varies widely or multiple circuit points need to be connected, a loop feed transformer may be a better choice.
System reliability: Loop feed transformers offer more redundancy and flexibility, as they can be operated in parallel and can continue to supply power even if one transformer fails or needs maintenance. Radial feed transformers, on the other hand, are more vulnerable to single-point failures, which can lead to power outages.
Efficiency: Loop feed transformers can be more energy-efficient, as they can be operated in a way that minimizes no-load losses and reactive excitation currents. Radial feed transformers, on the other hand, may have higher losses due to their simpler design and lack of load-balancing capabilities.
Cost: Radial feed transformers are generally simpler and less expensive than loop feed transformers. However, the cost difference may be offset by the need for additional equipment or redundancy in the power distribution system.
Ultimately, the choice between a loop feed and radial feed transformer depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the power distribution system. It's important to consider factors such as load characteristics, system reliability, efficiency, and cost to determine the most suitable transformer for the application.
View Single Phase Pole Mounted Transformer Information
Electrical transformer manufacturer (Daelim)
For over two decades, Daelim has been committed to providing high-quality transformer solutions to our customers, and as a result, Daelim have gained a reputation for excellence and reliability. Our dedicated team has worked tirelessly to earn the trust of customers in North and South America through exceptional service and attention to detail.
Daelim specialize in providing ideal solutions for a range of industries, including solar power, wind power, energy storage, mining and utilities. Whether you need support for a new project or are looking to upgrade your existing systems, we are always available to help.
At our core, Daelim dedicated to improving the efficiency and sustainability of power systems, while ensuring that you receive the highest level of support and service possible. Contact daelim at [email protected] to learn more about how Daelim can help you achieve your goals."
Related Products
Related Article
Pad Mounted Transformer CSA C227.4 National Standard of Canada
As a transformer buyer and manufacturer, you should be familiar with the local transformer design requirements and standards. This article tells the Canadian country's transformer standard CSA C227.4, the pad-mounted transformer below 3000kva.
CSA C802 For Minimum Efficiency Values For Power Transformers
The Canadian Standards Association has issued and produced CSA C802 as a national standard and policy for the country. This policy explicitly shows the performance and efficacy levels of power transformers rated from 501 to 10000 kVA.
CSA C227.3 For Single Phase Pad Mounted Distribution Transformer
What we have here are the Canadian Standards Association standards. This will include the CSA-C227.3 guidelines for single-phase pad-mounted distribution transformers.









