Power Transformer-The Ultimate FAQs Guide

Power transformers are one of the most important equipment in the electrical power system. If you have any questions regarding power transformers, you'll find all of the answers you're looking for here.
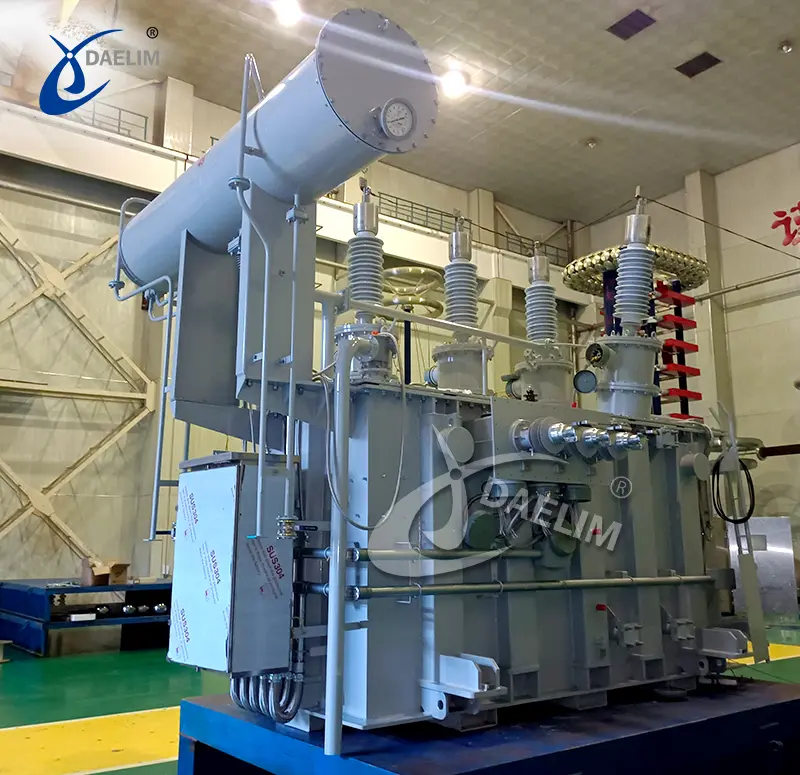
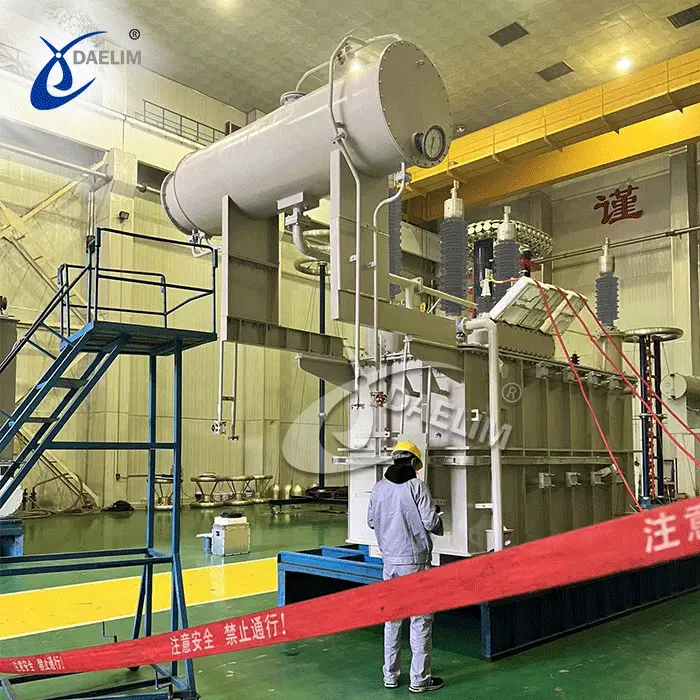
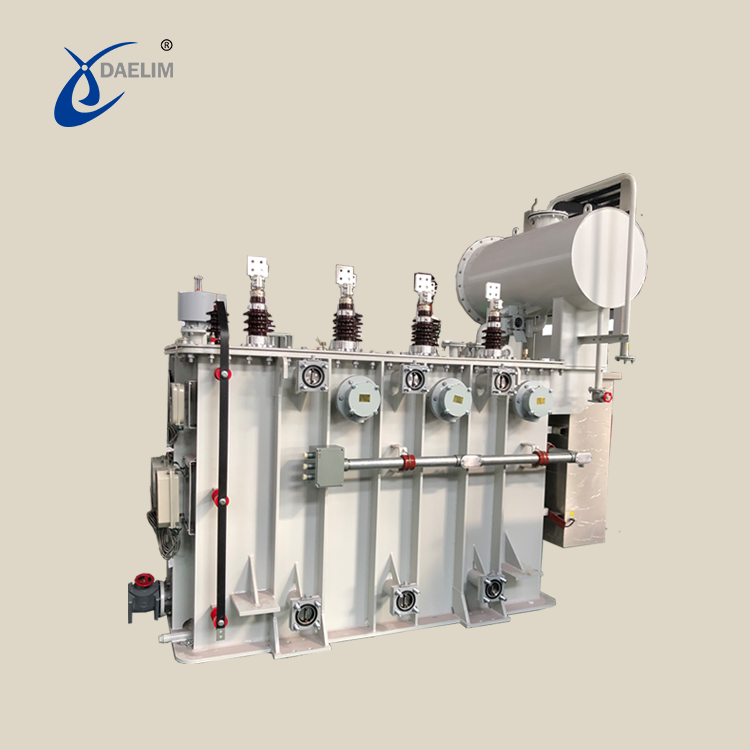
Daelim is a professional power transformer manufacturer in China. The voltage level is up to 230kV, and the capacity is up to 240MVA. Pad-mounted, substation transformer and single phase have UL/cUL, CSA, IEEE, and other certificates. The transformers designed and produced by Daelim comply with various international standards such as ANSI/IEEE, CSA, DOE, AS, and NEMA.
What is a power transformer in a substation?
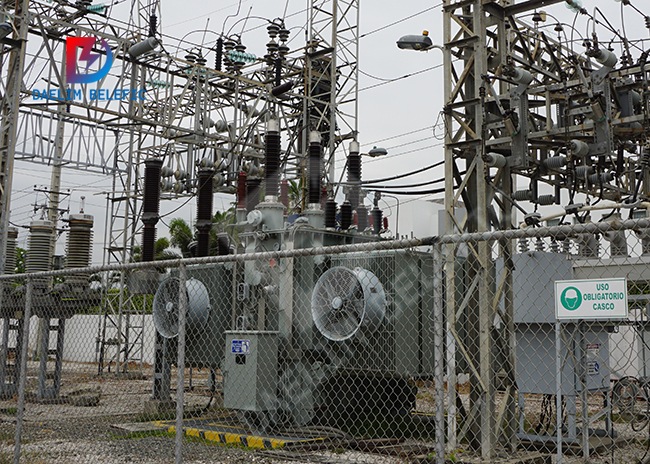

A power transformer is an industrial-grade electromagnetic device that harnesses the power of inductive coupling to transfer energy from one electrical supply circuit to another. It is the most important component in an electrical substation.
An electrical substation is a place where electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed to consumers. A power transformer is used to increase (step up) or decrease (step down) the voltage of an AC electrical supply.
Learn more: Electrical Power Transformer Basic Guide
Transformers typically use two or more coils of wire, called "windings," to transfer energy from one circuit to another. The windings are wrapped around a common iron core where the primary and secondary windings are connected to the power source and the load, respectively.
As the alternating current in the primary winding changes direction, it creates a changing magnetic field. This magnetic field produces the necessary energy for the secondary winding. The transformer's job is to transfer energy from the primary circuit to the secondary circuit with as little loss as possible.
What's the purpose of using a power transformer?
The main purpose of a power transformer is to convert high-voltage electricity into lesser and more manageable electric sources for both commercial and residential use. A transformer lowers the voltage rate from the power grid to a safer and more manageable level where the secondary winding can use this converted electricity to power businesses and homes.
The load might be a light bulb, a motor, or some other type of equipment. The transformer converts and maintains the proper voltage to ensure continuous use without potentially damaging the appliance.
The transformer can also increase the voltage if the load requires more juice than the current power available from the power grid. This is often the case with equipment that uses a lot of electricity, such as electric furnaces and large air conditioners.
In addition, power transformers can be used to change the voltage from one level to another. This is often done to transmit electricity over long distances.
Power transformer manufacturers hone their craft by designing transformers that minimize energy loss while providing the necessary voltage conversion.
Try for free: How To Buy Power Transformers In Australia?
How does a power transformer differ from a distribution transformer?

Both terms are commonly used interchangeably, but there is a technical difference between the two types of transformers. The clear difference between a power transformer and a distribution transformer is that the former is used during the load period while the latter operates in both load and no-load periods.
Distribution transformers are meant to step down the voltage from the power grid to a safe level for both commercial and residential applications.
In addition, distribution transformers are usually smaller in size than power transformers. This is because distribution transformers typically have a lower capacity than power transformers.
Read my article on How to choose the best distribution transformer?
How many power transformer types are there?
There are ten power transformers types:
Step-up power transformers
Step-down power transformers
Three-phase power transformers
Single-phase power transformers
Distribution power transformers
Instrument power transformers
Indoor power transformers
Outdoor power transformers
Oil-type power transformers
Dry-type power transformers
Step-Up Power Transformer
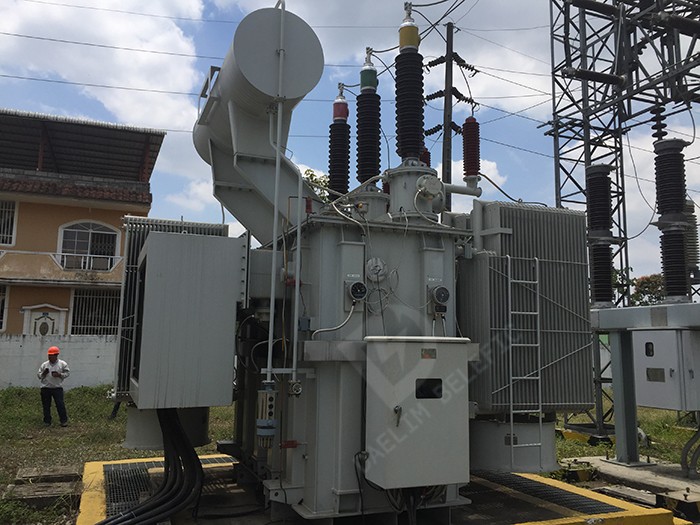

A step-up transformer is used to convert low-voltage (LV) and high-current (HC) electricity into high-voltage (HV) and low-current (LC) electricity. It transfers the power transformer's high-current, low-voltage primary side to the low-current, high-voltage value secondary side.
Step-up transformers increase the primary voltage to secondary voltage. As a result, the step-up power transformer's secondary winding will have more turns. This increases the transformers' capability to transfer energy and power.
Step-Down Power Transformer

Step-down transformers are the exact opposite of step-up transformers. It transforms high-voltage (HV) and low-current (LC) electricity into low-voltage (LV) and high-current (HC) electricity.
Simply put, step-down power transformers do the exact opposite of a step-up power transformer. Power transformers in substations have the ability to both increase and decrease voltages. However, its capacity will depend entirely on the purpose and situation.
The step-down transformer also has a secondary winding that has fewer turns than the primary winding. This results in the transformer having a lower capacity to transfer energy and power.
Keep reading: Step-up vs Step-down Transformer
Three-Phase Transformer
A three-phase transformer is a type of power transformer that's commonly used for projects that features a compatible three-phase power system. It's a more efficient way to transmit electricity compared to a single-phase power system.
Three-phase systems are often used in industrial and commercial settings where large amounts of electricity are needed. This is because three-phase systems can transmit more power than single-phase ones while using less conductor material.
One of the benefits of using a three-phase system is that it can provide a steadier and more constant flow of power. This is due to the fact that three-phase systems have three alternating currents that are offset by one-third of a cycle. This offset minimizes any gaps in the power supply, which results in a steadier flow of power.
Read on: 3 Phase Pad Mounted Transformer
Single-Phase Transformer

A single-phase transformer uses a single-phase alternating current. So it's heavily dependent on an operational voltage cycle that's generated by a single alternating current in a unified time phase.
Single-phase systems are often used in residential settings where lower amounts of electricity are needed. The primary to the secondary windings' electric ratio will determine the transformation the single-phase transformer can provide.
Daelim's single transformer has two types: single phase pole transformer mounted and single phase pad mounted transformer. A large number of exported to North America and Central and South America, mainly for power distribution in residential areas.
You may enjoy: 167 kVA Transformers: The Ultimate FAQ Guide
Distribution Transformer
A distribution transformer decreases the voltage of an electric power distribution system to the level that's compatible with the voltages that the customer uses. Various power transformer manufacturers typically use it for commercial or domestic purposes.
A distribution transformer usually has excellent voltage regulation levels that maintain a steadier voltage. This is because it typically features a tap changer that can automatically adjust the turn ratio of the transformer's primary and secondary windings.
This feature results in the distribution transformer having the ability to maintain a steadier voltage even when there are load changes. The tap changer is usually located on the secondary side of the distribution transformer.
Read more about distribution transformer: What Is Distribution Transformer?
Instrument Transformer
An instrument transformer is a type of power transformer that's used to isolate and change certain attributes of an electric circuit. These attributes can include voltage, current, or impedance. Instrument transformers are often used in industrial settings where electricity is measured or monitored.
One of the benefits of using an instrument transformer is that it decreases high currents and voltages to mitigate the values to a safer level. This is done by using either a current transformer or a voltage transformer.
A current transformer changes the high primary current into a lower secondary current. This is done by wrapping the primary conductor around a magnetic core and passing the resulting current through the secondary winding.
A voltage instrument power transformer converts the high-voltage primary side into low-voltage secondary side. This is done by placing the primary and secondary windings on different cores and passing the current through the primary winding. The newly converted voltage will then travel from the primary winding and through the secondary winding.
Indoor Transformer
An indoor transformer is a type of power transformer that's installed indoors. Indoor transformers are typically used in settings where there's a lower risk of fire or explosion. This is because indoor transformers are less likely to be damaged by weather conditions.
Indoor transformers are also often used in settings where aesthetics are important. This is because indoor transformers can be hidden from view more easily than outdoor transformers.
Outdoor Transformer
An outdoor transformer is a type of power transformer that's installed outdoors. Outdoor transformers are typically used in settings where there's a higher risk of fire or explosion. In addition, outdoor transformers are more likely to be damaged by weather conditions.
Outdoor transformers are also often used in settings where space is limited. This is because outdoor transformers take up less space than indoor transformers.
Oil-type Transformer

As the name suggests, an oil-type transformer is a type of power transformer that uses oil (transformer or mineral oils) as a coolant. Oil-type transformers are often used in settings where there's a need for a high degree of protection. This is because oil-type transformers are less likely to catch fire than air-cooled transformers.
Get it now: How much do you know about oil-immersed distribution transformers?
Dry-type Transformer
A dry-type transformer is a type of power transformer that uses air as a coolant. Dry-type transformers are often used in settings where there's a need for a lower degree of protection. This is because dry-type transformers are more likely to catch fire than oil-type transformers.
In addition, dry-type transformers are more affordable than oil-type transformers. This is because dry-type transformers don't require the use of expensive oil as a coolant.
Reading on: Ultimate guide of cast resin dry type transformer
How does a power transformer work?
A power transformer converts the voltage of an electrical power supply. The primary winding of a power transformer connects to the AC power source, while the secondary winding is connected to the load.
The transformer uses the principles of electromagnetic induction to convert winding voltages from the primary winding to secondary. This concept creates a magnetic field, producing the optimal voltage.
Without a power transformer, electronic equipment would not be able to function properly. At the same time, power transformers help to protect electronic equipment from damage by regulating the voltage of the power supply.
Try for free: Basic Guide To High Voltage Power Transformers
What are the different uses and applications of a power transformer?
Power transformers are used for the following applications:
Power generation and distribution.
It is increasing the voltage of an electrical supply to transmit electricity over long distances.
Decreasing the voltage of an electrical supply to make electricity safe for use in homes and businesses.
Isolating two electrical circuits from each other to safeguard sensitive electronic equipment.
Providing sufficient power to electronic equipment that requires a lot of electricity.
Sustaining the voltage of an electrical supply during power surges and brownouts.
Converting the voltage of an electrical supply from one country to another.
Reducing power losses during the transmission and distribution of electricity.
Used in cases where the load is required to have a different voltage than the supply.
There are numerous applications for power transformers, which is why they are essential components of the electrical grid.
Learn more: Solar Transformer - Your ultimate guide
What is a 66kv transformer?
 A 66kv transformer is a power transformer that's designed for low-loss, high-efficiency power transfer at 66,000 volts. The transformer is made of two or more windings wound around a common magnetic core.
A 66kv transformer is a power transformer that's designed for low-loss, high-efficiency power transfer at 66,000 volts. The transformer is made of two or more windings wound around a common magnetic core.
A 66kv transformer usually has the lowest kilovolt ampere rating (kVA) of any standard transformer. This is because the transformer is designed for lower losses and higher efficiency.
Some of the key features of a 66kv transformer include:
Dielectric strength of 66kv.
A frequency range of 50 to 60 Hertz.
A maximum power rating of 500 kVA.
A maximum voltage rating of 66,000 volts.
A minimum impedance of 0.25%.
Daelim 66kV transformers have been exported to Australia, Canada, Myanmar, and other countries. Daelim 69kV transformer and substation projects are numerous in Ecuador.
69KV Series Substation, Latin America
What is a 138kv transformer?
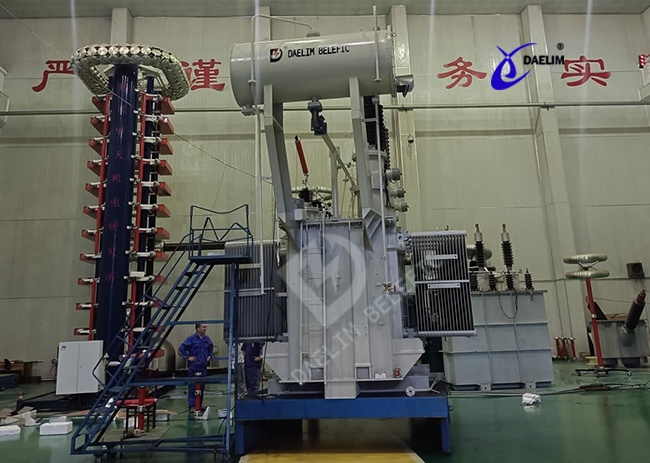

A 138kv transformer is an optimized transformer that's designed to absorb and utilize advanced reactive power compensation techniques. The optimized transformer core, body, coil, and fuel tank, among other components, help to make the 138kv transformer one of the most efficient and reliable power transformers available.
Some of the key features of the 138kv transformer include:
Reduced no-load and eddy current losses.
Higher impedance design for superior voltage regulation.
Lower sound levels.
Windings are made of copper or aluminum for better conductivity.
Enhanced mechanical strength and durability.
Read on: How To Choose The Suitable 110KV Power Transformer?
What is a 220kv transformer?
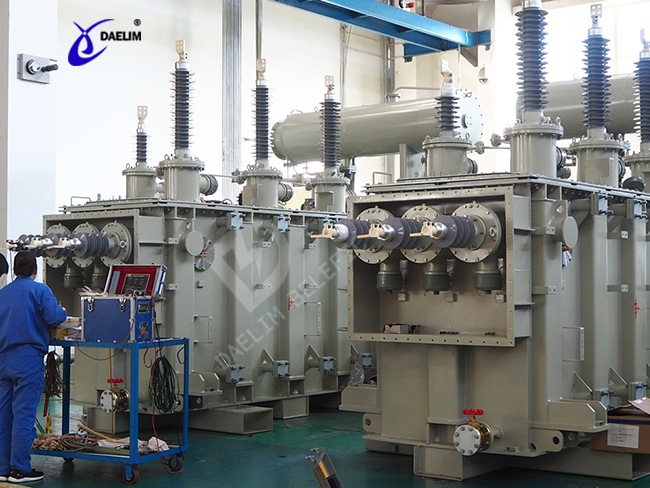

The 220kv transformer is a power transformer that's designed for high-voltage, long-distance power transmission. The 220kv transformer is made of two or more windings wound around a common magnetic core.
A 220kv transformer usually has a higher kilovolt ampere rating (kVA) than other standard transformers. This is because the transformer is designed for high-voltage power transmission.
Some of the key features of a 220kv transformer include:
High security and reliability during operation
High economic efficiency to reduce power losses
A wide voltage regulation range
High insulating and short-circuit strength
Customize transformers to meet your specific needs
Excellent short delivery times
No-load and eddy current losses are low
Daelim 220kV transformers are exported to many units in Ecuador, and there is a local after-sales installation team. Daelim 230kV transformers are exported to the United States, and 115kV transformers are exported to Mexico and other countries.
In conclusion
Every transformer produced by Daelim has to go through strict quality control. Including routine tests before leaving the factory, routine tests, and some special test items according to customer requirements. Pursuing high-quality products is the philosophy of the Daelim transformer enterprise. If you have any technical and price questions about the transformer, please contact the Daelim team, Daelim will reply within 8 hours.
Related Products
Related Article
Basic Guide for Grounding Transformer
In the three-phase power system, grounding transformer plays the role and function of auxiliary transformer. The function of a grounding transformer is to provide grounding mode for ungrounded delta connect or wye connect. Therefore, a ground transformer is also a very important part of the power grid grounding system.
Solar Transformer, Get The Best Price
Solar energy is the most abundant energy source on earth, and contemporary solar energy can be used to produce other renewable energy sources. We can convert solar energy into electricity. At present, there are two main conversion forms in the world, one is solar photovoltaic power stations, and the other is solar thermal power stations. Whether it is photovoltaic power generation or solar thermal power generation, solar transformers are used.
What do you need to know about power pole transformer ?
Power pole transformer refers to a power transformer installed on a wooden pole or a concrete pole. Power pole transformer is often used to reduce the voltage of distribution level to the consumption level, with the purpose of supplying power to nearby residential areas or residential areas.















