Beginner Guide To Iron Core Transformer

Electrical transformers consist of many parts and one of the major parts of an electrical transformer is its Core. The core plays an important role in transferring the magnetic flux between primary and secondary winding. The working and efficiency of the transformer core depends mainly on two things. One is the design or configuration of the transformer Core and second is the material from which the core is constructed.
Due to some major design constraints there are only a few fixed configurations in which the Transformer core can be constructed. So the major difference in different types of transformer core lies in the quality and type of material used for the construction of the transformer core.
In this article we will study Iron core transformers, one of the most widely used transformers in the transformer industry. We will analyse what material properties does iron core Transformer have that cores made from other material cannot offer. We will analyse different types of iron core Transformers, manufacturing process involved in manufacturing of iron core transformers, advantages, disadvantages and applications of iron core transformers.
Contact Daelim TransformerWhat is an Iron Core Transformer?
By the iron core transformer definition, it is a type of electrical transformer that uses a core made of iron. Thin iron sheets that have proper lamination for insulation purposes are used for core construction. Each sheet is first precisely cut into required shape and then stacked up to get a specific configuration of the transformer core.
The iron material in the transformer core acts as a low resistance path for transfer of magnetic flux from primary to secondary winding section of the transformer. This low resistance path increases the magnetic coupling of windings that improves the efficiency of the transformer core and thus the overall efficiency of the transformer to a great extent.
Iron Core Transformer Symbol
In the electrical circuit diagram the iron core transformer is represented with a unique symbol where there are two coils (representing transformer windings) placed very near to each other with two straight, vertical and parallel lines between them. The iron core inductor symbol is shown below. The two straight, vertical and parallel lines represent iron core and this distinguishes it from air core transformers that do not have these two straight, vertical and parallel lines.
Iron Core Transformer Function
The main function of the iron core in the iron core transformer is to transfer the magnetic flux from primary to secondary transformer winding with minimum losses called core losses. The iron core is responsible for transferring the magnetic flux from one winding to another while maintaining the frequency at which the voltage was applied to generate magnetic flux.
If we consider the working principle behind this, then iron core like any other transformer core works on the principle of Faraday's law of Electromagnetic induction where iron core uses the magnetic field created by the electrical voltage in the primary winding to induce the voltage in the secondary winding of the electrical transformer.
Why Soft Iron is Used in Transformers
There are three main reasons why soft iron is used as the main material in the transformer core and all three are mainly due to the material properties of the soft iron.
High Magnetic Permeability
Due to excellent material conductivity, the soft iron has the ability to transfer the magnetic flux that is needed to step up or step down voltage much more easily and efficiently. Soft iron core efficiency is much more than that of the air core or core made from non-magnetic materials.
Low Core Related Losses
The iron core is made from thin iron sheets that are first laminated and then cut and assembled into required configuration. Iron sheets when laminated offer minimum resistance in transfer of magnetic flux thus reducing all types of losses like core losses, hysteresis and eddy current losses.
Learn more about Losses in Transformer
Easy Magnetization and Demagnetization
Due to excellent electrical and soft material properties of the soft iron core material, it magnetizes and demagnetizes very easily which makes it very ideal for all types of alternating current applications. This is because in alternating current applications, the polarity reverses continuously and thus needs material that can magnetize and demagnetize easily and quickly.
Types of Iron Core Transformers
The iron core transformers are broadly divided into two main types based on the structure or construction of the core.
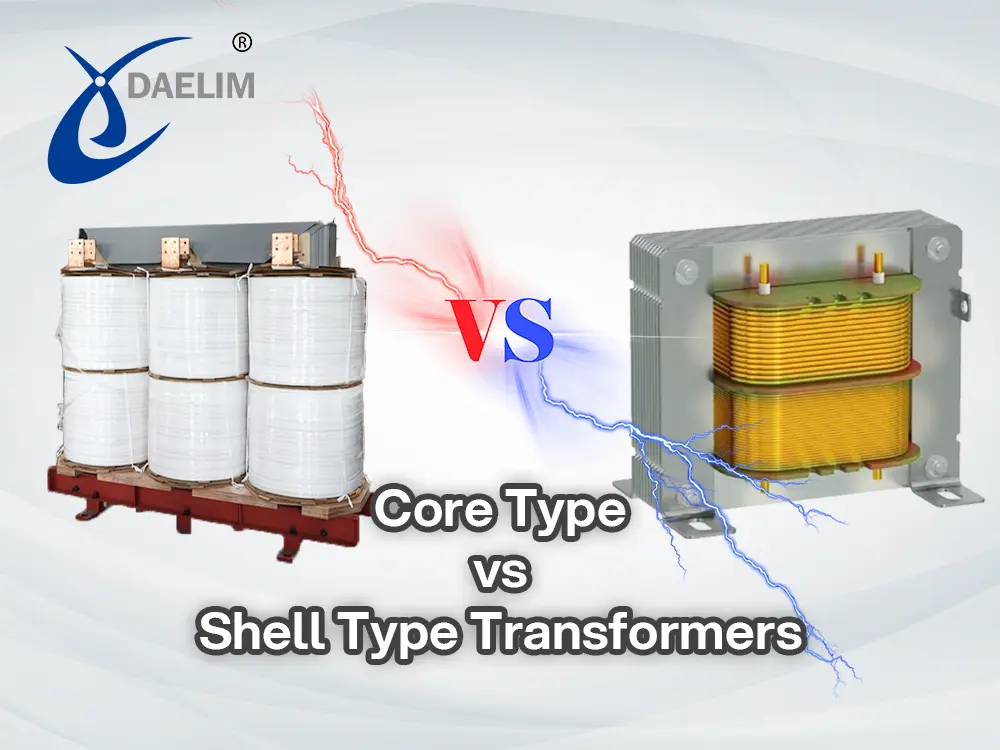
Core Type Transformer
In core type iron core transformers, the iron core is constructed in core configuration. Core configuration is a specific shape of core in which the transformer winding is wound around the laminated sheet of iron core limbs. The iron core in this configuration looks like a square or rectangular frame. The winding coils are wound on the opposite sides (limbs) of the core.
Reading more about Core Type Transformer
Shell Type Transformer
 In shell type iron core transformers, the iron core is constructed in shell-like configuration. Shell-like configuration is a specific shape of core in which the transformer winding is wound around the laminated sheet of iron core limbs. The iron core in this configuration has a frame made from a combination of two parts where one looks like the English alphabet E and the other looks like the English alphabet I. It can also be made from a square frame with a horizontal center bar. The winding coils are wound on the center limb (horizontal center bar) and on two opposite sides (limbs) of the core.
In shell type iron core transformers, the iron core is constructed in shell-like configuration. Shell-like configuration is a specific shape of core in which the transformer winding is wound around the laminated sheet of iron core limbs. The iron core in this configuration has a frame made from a combination of two parts where one looks like the English alphabet E and the other looks like the English alphabet I. It can also be made from a square frame with a horizontal center bar. The winding coils are wound on the center limb (horizontal center bar) and on two opposite sides (limbs) of the core.
Comparison between Iron Core Transformer of Core Type and Shell Type
| Feature | Core Type | Shell Type |
| Magnetic path | Single path | Multiple paths |
| Coil arrangement | Windings surround core | Core surrounds windings |
| Cooling efficiency | Better | Moderate |
| Applications | High-voltage | Low to medium-voltage |
Keep reading: Core Type vs Shell Type Transformers
Manufacturing of Iron Core Transformers
The manufacturing process of iron core transformers can be different for different configurations; however, irrespective of the configuration, the iron core inductor manufacturing has several basic yet key steps to ensure quality manufacturing and durability of the final product.
Material Inspection and Quality Check
The first step in the manufacturing of iron core transformers is the material inspection and quality check of the thin iron core sheets supplied to the manufacturing facility. The manufacturing facility needs to ensure that the sheets of soft iron have the required thickness and they are free from any type of defects that might cause loss of efficiency or product failure in the future. This phase includes performing a number of tests on the material like electrical conductivity test, material tensile strength test, fatigue test, and ultrasonic inspection.
Lamination of Soft Iron Sheets
The second step in the manufacturing of iron core transformers is the lamination of soft iron sheets that are delivered to the manufacturing facility. The lamination is done to ensure the insulation of each sheet against the external environment, the transformer winding, and with other sheets that are used in core manufacturing.
It is the responsibility of the manufacturing industry to ensure that the lamination of the sheets is done properly and no part of the sheet is exposed because it can cause loss of efficiency and permanent failure in the electrical transformer.
Core Assembly Process
After ensuring that the material supplied for the iron core transformer manufacturing is of high quality and the lamination of the iron core sheet has been done properly, it is time to start the manufacturing and assembly process of the transformer core.
The first step in this regard is the cutting of the laminated thin soft iron sheets into the required shapes. A computer numeric control laser cutting or a punch press machine is used to cut the sheets into required shapes. This process has to be done in a very precise manner as each sheet of the soft iron has to be cut to the exact same size and shape. Any mismatch between the sheets can result in serious loss of efficiency and permanent damage in the future.
After the cutting process, all the newly cut sheets are collected and stacked together to form the initial shape of the transformer core. This stacking of laminated thin iron sheets to form the core of the iron core transformer is followed by an overall insulating coating to reduce any eddy current losses.
Magnetic Core Treatment
After assembling the core of the soft iron core transformer, it is time to increase the strength of the transformer core by processing it through a heat treatment process called annealing. In this process, the core material is first heated to a specific temperature and then maintained at that elevated temperature for a specific period of time.
After that, the entire core assembly is cooled in a controlled manner to remove all types of internal stresses that might have been produced during the cutting and stacking of thin iron sheets into the core shape. This treatment process also improves the magnetic properties of the soft iron and increases the efficiency of the iron core in transferring the magnetic flux between windings.
Working Principle of Iron Core Transformers
The working principle of an iron core transformer is exactly the same as that of any other transformer, and that is, it works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When we apply alternating current on the primary winding of the soft iron core transformer, that applied voltage produces a magnetic field in the iron core. Now, as the alternating current was applied, the magnetic field is also changing continuously, which magnetizes and demagnetizes the soft iron core transformer. The iron core of the transformer transfers that changing magnetic flux from primary to secondary winding where that magnetic flux is used to induce an alternating current in the secondary winding.
Advantages of Iron Core Transformers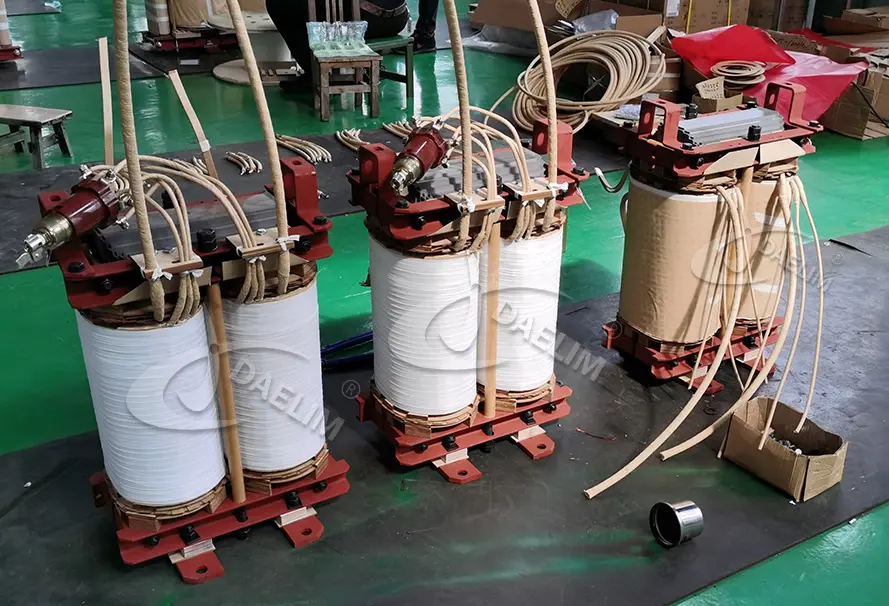
There are several advantages to why soft iron core is used in transformers over other conventional and traditional transformers and their cores. Some of the advantages of the iron core transformer are as follows.
- The iron core transformer has high efficiency as compared to other similar transformers, and this is because this transformer has much lesser core losses and other associated transformer losses.
- One of the best advantages of having an iron core transformer is its reliability in voltage transformation. The iron core transformers are capable of maintaining the voltage level irrespective of the application with minimum fluctuation.
- The iron core transformers are considered ideal for high-load industrial applications where heavy-duty industrial machinery is being used.
- These transformers are also considered very cost-effective as the main material used in the construction is iron, which is very easily and widely available and is the most cost-effective material in the industry.
You may enjoy: What different materials are used in a Transformer?
Disadvantages of Iron Core Transformers
Like other industrial products, the iron core transformer also has its own disadvantages. Following are some of the disadvantages of having an iron core transformer.
- The biggest disadvantage of iron core transformers is that these transformers are always very heavy, bulky, and large in size. This is because iron itself is a very dense material, and the addition of the lamination of the iron core adds significant weight and volume to the final transformer size and weight.
- When we compare the conventional iron core transformer with sensitive and modern transformers that are widely used in sensitive applications, the iron core transformer is a bit less efficient compared to these modern transformers.
- Another disadvantage of having an iron core transformer in indoor applications is that these transformers produce an audible noise during their operation. This noise is due to vibrations that happen during the magnetic changes.
Applications of Iron Core Transformers
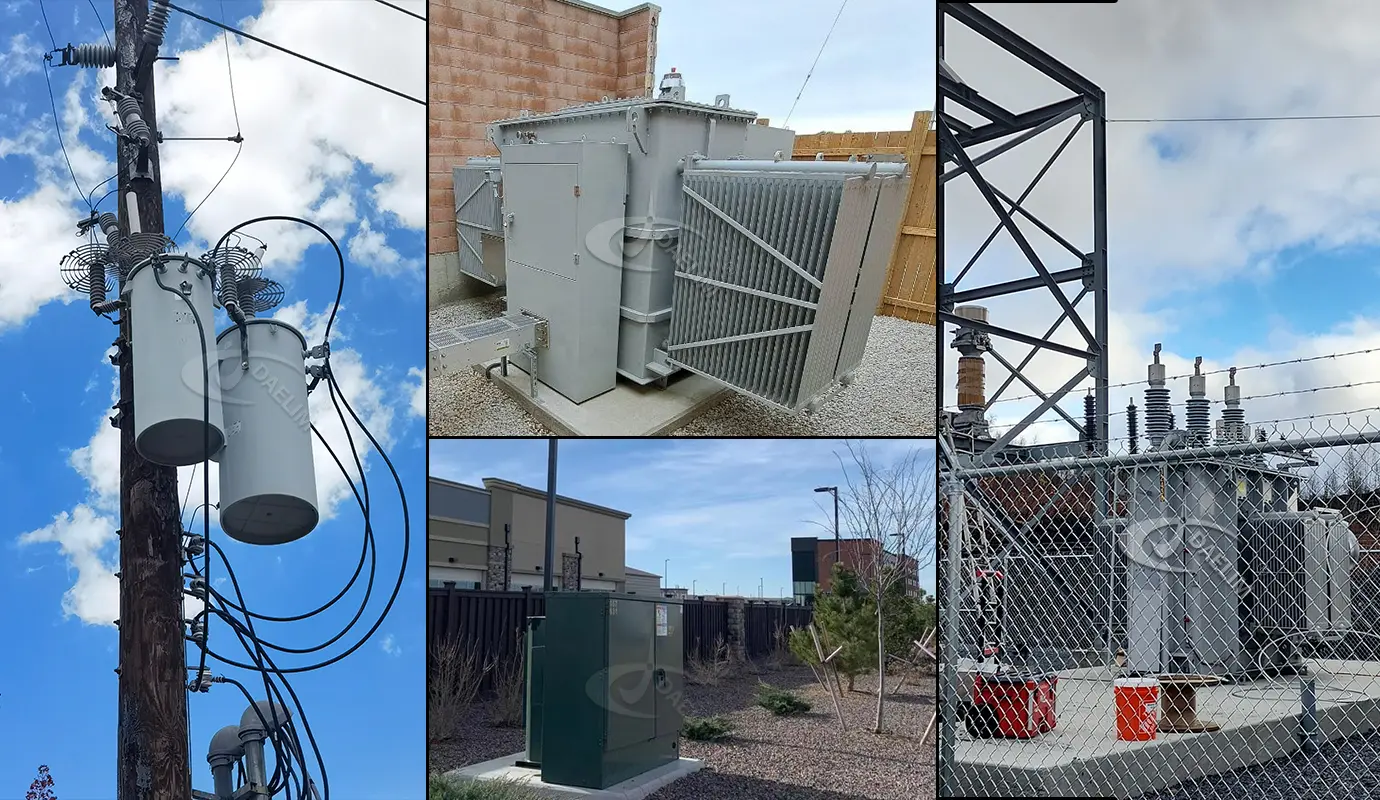

The iron core transformers are very widely used in different industries to support various industrial machinery and products due to their robustness and high efficiency. Some of the common applications of iron core transformers are as follows.
Iron core transformers are very widely used in power transmission and electricity distribution systems; they are always a main part of national grid-related power transformers.
These transformers are always used to support industrial machinery like motor starters, drives, and other control panels that need reliability and stability in electricity supply.
These iron core transformers are also sometimes used in residential and commercial applications where they are used to regulate electricity for a vast area.
Get it free: Different Transformer Types and Their Applications
Iron Core Transformers vs Other Core Types
Iron Core vs Air Core
| Feature | Iron Core | Air Core |
| Magnetic Flux | High | Low |
| Efficiency | High | Low |
| Applications | Power systems | High-frequency, low-power RF systems |
Iron Core vs Amorphous Core
| Feature | Iron Core | Amorphous Core |
| Core Loss | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Industrial Use | Common | Gaining popularity in smart grids |
Iron Core vs Ferrite Core
| Feature | Iron Core | Ferrite Core |
| Frequency Range | Low | High |
| Heat Dissipation | More | Less |
| Applications | Power transformers | Switch-mode power supplies, RF circuits |
Conclusion
Iron Core Transformers remain an important part of our Transformer Industries as these Transformers are reliable and highly efficient in regulating electricity for a range of applications. The iron core Transformers or consider highly durable, cost effective and efficient in regulating electricity as compared to many other types of electrical Transformers. The manufacturing process of these electrical Transformers is not much different from others, however they are some key considerations that we should keep in mind. The iron core Transformers also have unique advantages that increase losses and easy magnetising and demagnetising while at the same time they offer disadvantages like increasing weight and size.
Follow Up

Daelim Transformer offers iron Transformers of all types and sizes that can satisfy any International standards like that of IEEE, IEC and ANSI. Our transformers are made from high quality soft iron thin sheets that are laminated using automated processes to ensure efficiency and reliability. If you have any questions related to the iron core Transformers, you can Contact our team and they will talk with you about the process.
Related Products
Related Article
Core Type vs Shell Type Transformers
Core-type and shell-type transformers differ in structure, magnetic path, conductor material, and cooling efficiency. Core-type transformers offer better insulation, easier maintenance, and cost-effectiveness for high-power applications. Shell-type transformers, with a shorter magnetic path and compact design, provide higher efficiency and superior heat management. While core-type transformers excel in industrial use, shell-type transformers are ideal for space-saving and energy-efficient solutions. Choosing the right transformer depends on application needs, cost considerations, and performance efficiency.
Comparing Amorphous Core and Silicon Steel Core Transformers
Amorphous and silicon steel cores are key transformer materials. Amorphous cores offer lower core losses, higher efficiency, and are ideal for energy-efficient, eco-friendly applications, but are costly and fragile. Silicon steel cores are cheaper, durable, and suitable for high-power, mass applications, though with higher losses. Choice depends on efficiency needs versus cost considerations.
How Transformers and PDUs Work Together for Data Center Power
In data centers, uninterrupted power is crucial. Transformers step down high-voltage grid power to usable levels, while PDUs distribute it to IT infrastructure. Together, they maintain continuous, efficient power flow, preventing costly disruptions even during brief outages.
How much electricity is lost in Transmission
When electricity is transmitted from a utility to consumers, some energy is inevitably lost, making it a costly aspect of modern power systems. These losses occur during transmission and distribution, affecting both energy efficiency and operating costs. Annually, about 5–8% of generated electricity is lost, highlighting the need for improved infrastructure and energy management strategies.
Transformer Overcurrent Protection
A transformer is vital in power distribution and industry but vulnerable to overcurrent faults from overloads, short circuits, or system issues. Such conditions can damage components, shorten lifespan, and cause financial losses. Hence, overcurrent protection is not optional but essential to ensure reliability, safety, and cost efficiency in transformer operations.
Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Transformers for Blockchain
Reliable electricity is essential for blockchain. A key factor in every successful mining farm is the right transformer. Whether for small setups or large-scale industrial blockchain operations, choosing an efficient, dependable transformer ensures stable power, maximizes performance, prevents costly downtime, and supports the growing energy demands of blockchain infrastructure.